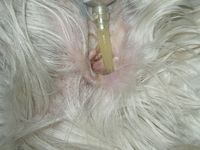
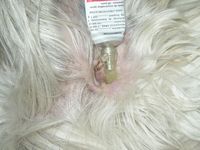
Ear infections
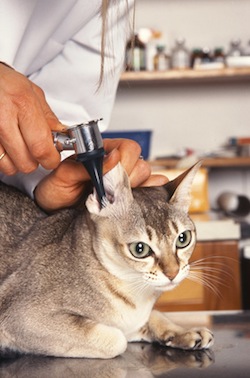 Otitis media is an inflammation of the ear canal. It's an extremely common pathology in our domestic carnivores. It can have many origins which some will be responsible for recurrent ear infections.
Otitis media is an inflammation of the ear canal. It's an extremely common pathology in our domestic carnivores. It can have many origins which some will be responsible for recurrent ear infections.
Some useful information…
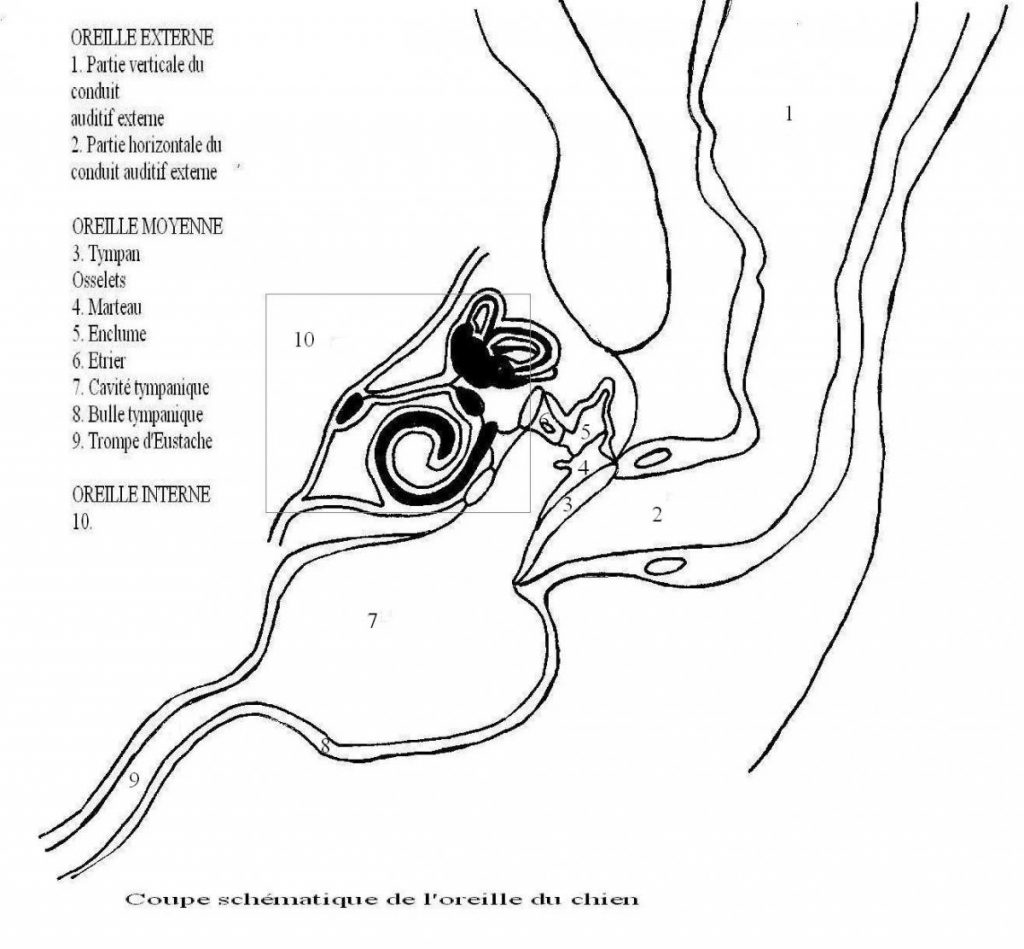
¤ The outer ear is the organ of perception of sound waves.
It features the atrial flag and led auditory external. Domestic carnivores, This duct has the shape of an L.
¤ The eardrum is a thin membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear.
¤ The middle ear is the body for transmission of sound waves.
It includes the eardrum, the ossicles, the eustachian tube and the Bulla.
¤ The inner ear is the body :
– perception of sound waves (It ensures the sound into an electrical signal transduction)
– and equilibration (It plays a role in the perception of the position of the body in space and thus ensures the balance of the whole body)
Different types of ear infections
Otitis externa
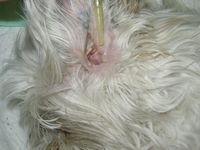
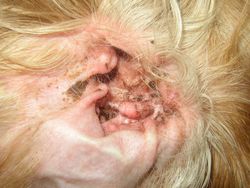 It is a inflammation of the external ear canal up to the ear drum. It is extremely common in our pets.
It is a inflammation of the external ear canal up to the ear drum. It is extremely common in our pets.
It is accompanied by significant itching. The animal rubs or to shake the ears permanently. It may experience a sharp pain and deny that examines his ear.
Depending on the cause and the stage of evolution of otitis, a sharp pain, Brown to blackish or even pus secretions can be seen at the edge of the ear canal. A very bad smell is often associated with these secretions (smell of rancid butter).
Otitis media
Otitis media is bound to a condition that concerns the tympanic bubbles.
It can be associated with an external ear infection but can also relate exclusively to the middle ear. In this case, no flow or no abnormality is perceptible to the direct examination of the ear canal.

Nevertheless the animal will present various symptoms suggestive of otitis media :
As in otitis externa, will be noticed :
¤ Signs of itching and pain :
– the dog or the cat complains as soon as it touches the base of his ear
– it stirred the head
¤ A gene and a sharp pain may be observed when the animal chewed or opened mouth.
It can, also suffer from :
¤ deafness
¤ sneezing or runny nose
¤ inflammation of any of the ENT
¤ Neurological with :
– Decrease in the production of tears
– Paralysis of one half of the face (one side of the face seems like "released" with a lid which remains mi-close and a drooping babine who let sink saliva)
Finally, a head maintained permanently leaning can be highly suggestive of the presence of otitis media.
Otitis internal
It is less common and is not discussed in this article.
The various causes of ear infections
Bacterial or fungal ear infections
Several types of bacteria (Staphylococci, Pseudomonas…) and yeast (Malassezia) can develop in the ear canal, causing the appearance of an ear infection.
These ear infections are so associated with purulent secretions and a very unpleasant smell.
Several factors will foster these ear infections :
The ear canal is located, under normal conditions, at constant temperature and humidity.
It contains, Furthermore, a particular microflora (specific yeasts and bacteria, present in a natural way in the ear, ensure a certain balance and the absence of onset of infection)
Anything that will destroy this natural flora and amend the conditions of humidity and temperature of the ear canal will promote development of yeast and bacteria causing the appearance of inflammation and therefore of an ear infection.
This is the case then :
– Too frequent cleaning, too "strippers" ears or made with unsuitable products
– Presence of "wads of hair" at the edge of the ear that obstruct the ear canal, causing the accumulation of ear wax, important maceration and secondarily infections.
– Swimming repeated animal penetrative frequent water in the ears (the "dog bather" syndrome)
– Deep bites close to the ear (especially during fights between cats) that will fester and encourage the development of pathogenic bacteria in the ear
– infectious lesions of the face that, untreated, will be able to extend up to the ear.
Parasites
Some parasites can be at the origin of the occurrence of otitis due to inflammation that they generate in the ear canal.
The most frequently encountered parasite is a mite called Otodectes cynotis responsible for "ear scabies"
(see article entitled ear mange)
This parasite is very contagious and his presence should especially be suspected when a new pet at home or in animals have access to outside and so frequently in contact with conspecifics (Explorers cats…)
Other parasites such as the "chiggers" or the demodex can also favour the appearance of ear infections.
Foreign bodies
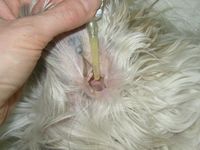
 Small foreign bodies such as spikelet of grasses can become lodged in the ear canal including following a walk in tall grass or a hunting party.
Small foreign bodies such as spikelet of grasses can become lodged in the ear canal including following a walk in tall grass or a hunting party.
(Read also “attention to the spikelets!”)
These foreign bodies are going to cause inflammation or infection and may go up to puncture the eardrum and create otitis media.
An ear infection caused by a foreign body is unilateral.
Allergies
Animals with an allergic field are particularly susceptible to ear infections.
Indeed, as humans, some dogs or cats will be "hypersensitive" to certain elements.
The substances of these allergies can be original :
– food
– environmental (mite allergy, pollen, to flea…)
These allergies promote significantly the occurrence of ear infections.
Otitis media will sometimes be the only suggestive sign of allergy, but it is most often associated with other clinical signs such as severe itching, skin disorders in other parts of the body, in particular the eye-rims, the ends or even all areas of very thin skin.
Ear infections caused by these allergies are of a recurrent nature.
Tumors and polyps
Tumors and inflammatory polyps of the ear canal are fairly rare in dogs but are encountered frequently in cats.
– Tumors ear canal generally affect older cats (10 years on average). They are most often malignant and/or they may concern the external ear and the middle ear.
– Inflammatory polyps are smooth masses, Roses, benign which develop in the ear canal, most often in young cats.
These are the most frequently encountered masses in the ear in cats.
They can be directly seen by examination of the external ear canal if they develop in the outer ear but can also take birth in the middle ear (at the level of the eustachian tube) or in the naso-pharynx (at the bottom of the throat)
The animal reaches presents signs of ear infection if the external ear canal is concerned, neurological signs if the mass is present in the middle ear or respiratory signs if the polyp originates in the naso-pharynx.
Polyps may be present in the kitten from birth or develop in response to inflammation, an infection of the respiratory tract (rhinitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis…) involving virus or bacteria that are progressing to the ear.
These polyps develop, most often, in one ear.
Other causes
So-called autoimmune diseases or certain dysendocrinies (as hypothyroidism) will also encourage the development of ear infections.
Very many causes can cause inflammation and infection of the ear canal.
Any otitis, especially when it is chronic, must be accompanied by an attentive research of one of these factors.
Diagnosis
¤ One otitis externa is evidenced by an examination of the ear canal using a Otoscope.
This review shows inflammation of the ear canal as well as the possible presence of secretions, Verify the absence of visible mass or foreign body in the ear and observe the status of the eardrum.
During recurrent or persistent ear infections, scrutiny cytobacteriological secretions in the ear will let know if yeast are involved, If bacteria are present and, in this case, What family of antibiotics will be most effective to eliminate.
¤ Duringmiddle ear infections, the otoscope examination may reveal abnormalities but, most of the time, the ear looks quite normal because the lesions are located behind the eardrum.
Diagnosis of otitis media requiring then other tests such as
– of x-rays (one or two tympanic bubbles appearing abnormal(s) on the cliché)
– examinations such as CT or MRI
Treatment
The treatment of an ear infection is to :
– Combat inflammation
– Eliminate bacteria and yeasts when they are present in the ear canal
External otitis
At otitis externa, local treatments will be instilled in the ears.
Multiple rules must be observed to ensure cure ear infections :
– The veterinarian performs at the clinic a thorough cleaning of the ear canal. You will then need to perform, You too, one regular cleaning ears to allow healing of your pet.
Indeed, excess Earwax and cellular debris which stagnate at the bottom of the duct support, not only, secondary infections but they also prevent direct contact between the wall of the ear canal and the processing product, What decreases very much the action of the latter.
It is therefore recommended to clean the ears of your pet all the 3 or 4 days to remove these dirt.
Do not use cotton swabs that will repel the secretions in the bottom of the duct. A cleaner atrial suitable for domestic carnivores will allow taking off this ear wax in the ear canal, ear wax which is then removed with a simple piece of cotton.
– Local treating products are highly concentrated in antibiotics and anti-inflammatory and channellocal administration is therefore most suited to the treatment of otitis externa.
This treatment should, on the other hand, be carried out correctly in order to be effective.
As we mentioned previously, the duct of domestic carnivores has the shape of an L.
The introduction of ointments or medicated solutions only on the edge of the ear canal does not allow penetration until the eardrum.
It should be well insert the tip in depth in the ear (ear treatments tips are all flexible and adapted to the anatomy of the ear of dogs and cats). For this, the ear of the animal will be gently drawn upwards and tip, maintained vertical, slipped almost entirely in duct.
– Sometimes, very important inflammatory changes resulted in changes of the structure of the ear : The wall of the duct is then very thickened or calcified and the animal is complaining as soon as it touches, What makes the treatment very difficult.
Do not be discouraged particularly !
The veterinarian will then anesthesia to achieve a first careful cleaning of the ear and then he can put in place systemic anti-inflammatory treatment to reduce inflammation and allow you to, After these days of 'treatment of attack', an easier application of the local salary.
Middle ear infections
Local treatments do not penetrate through the tympanum. So they don't have interest in the treatment of otitis average if otitis externa associated.
Inflammation of the middle ear is, It, treated with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs administered systemically during 4 to 6 weeks.
In more advanced cases (otitis externa with extremely important changes of the ear or otitis average unresponsive to medical treatment), surgery may be necessary (lowering of the auditory, trepanning of tympanic bubbles or even removal of the ear canal in the most serious cases).
Treatment of the obstructing cause
The treatment of an ear infection must absolutely take account of a possible triggering factor which, If it is not detected, makes any illusory healing :
¤ Acaricide treatment must be part of the drugs used to cure a "gale's ears"
These treatments are available in the form of pipettes to apply on the neck of the animal (selamectin, mixture of imidacloprid and moxidectin) ointments to apply topically or .
These parasites being highly contagious, all the animals of the home must absolutely be treated.
¤ An ear infection due to the presence of a foreign body cannot heal until after the withdrawal of this foreign body
¤ When a hypersensitivity to certain elements is at the origin of ear infections, provisions must be taken to reduce the risk of allergy :
– A hypoallergenic food will be distributed at food allergy
– Flea products will be applied regularly and anti-allergic treatment (anti-mite treatments, anti-histamines, corticosteroids, desensitization…) will be used in parallel with the own treatment of otitis media in cases of hypersensitivity to environmental allergens.
Pitfalls to avoid…
My dog has now own ear. I stop the treatment
Attention, taking into account the auditory of our domestic animals L-shaped, only a small part of the pipe is visible to the naked eye.
The dog or cat may have stopped to scratch, to complain and his ear may seem perfectly healed while germs are still present in the bottom of the ear canal.
Any cessation of therapy should absolutely be preceded by a visit to the vet who will review the duct until the eardrum and may deem the healing of otitis.
A too rapid discontinuation of treatment will promote the persistence in the bottom of the duct of bacteria becoming progressively resistant to many ear treatments and causing new more and more difficult to cure ear infections.
My dog again has an ear. I'll deal with the product that the veterinarian had issued to me for its previous otitis media.
Any suspicion of otitis media must be accompanied by a visit to the vet.
Indeed, two successive otitis may not have the same origin.
Previous treatment will therefore not necessarily effective.
Worse, treat an ear infection without prior examination of the ear canal will prevent :
– to detect a foreign body
– to highlight a tumor or a polyp
– to view a injury to the eardrum (knowing that many local salary administration ear infections is formally contraindicated during perforation of the eardrum and can cause serious side effects)
§
At otitis, the established treatment effects are generally very fast and the signs of pain and itching disappeared often in just a few days. Given the plethora of tasks to accomplish on a daily basis and ceased animal complaints, otitis media is quickly forgotten and the duration of the treatment recommended by the veterinarian is often not respected.
Yet, a visit to the vet must absolutely take place for the realization of a careful examination of the ear canal and confirmation of cure of otitis media under penalty of rapid recurrence.